Biodiversity is essential for a healthy and balanced ecosystem, but it is under threat due to various factors such as habitat destruction, climate change, and poaching. Technology has emerged as a powerful tool to help conserve biodiversity by identifying individual animals, tracking their movements, locating animal and plant species, and assessing the status of habitats. In this article, we will explore the different ways technology can contribute to biodiversity conservation and the importance of making these technologies accessible to all countries.
Hyperspectral Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing
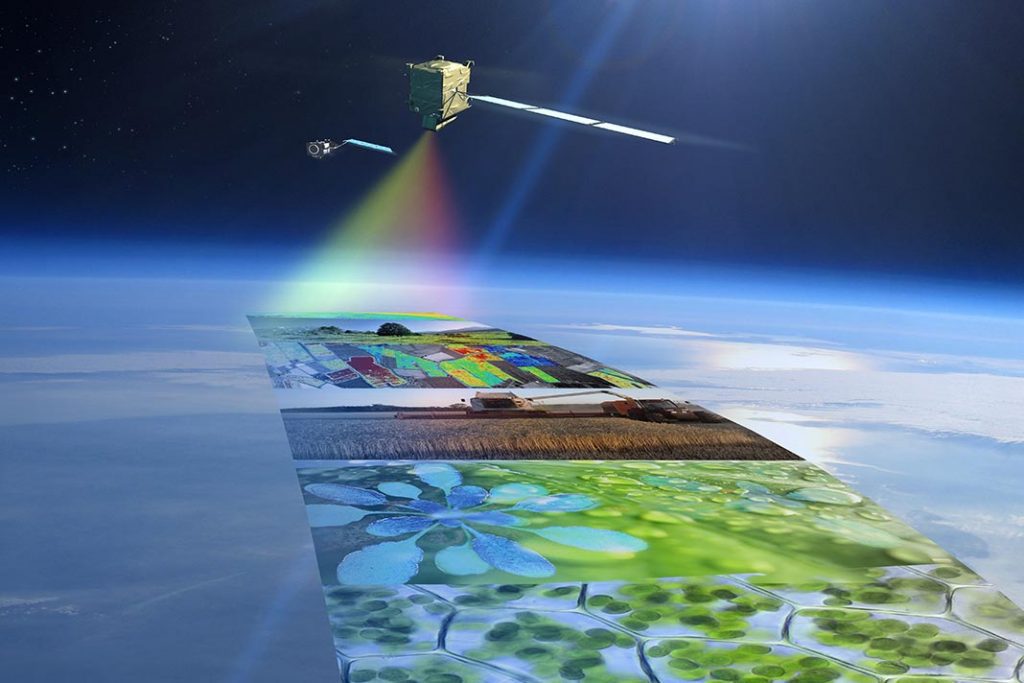
Hyperspectral satellite imagery and remote sensing play a vital role in conserving biodiversity by offering in-depth insights into the composition and health of ecosystems. Some hyperspectral sensors, equipped with over 200 bands, can deliver a wealth of information that aids in identifying specific species and monitoring changes in vegetation and land use.
By utilizing hyperspectral imagery and remote sensing, conservation biologists can maintain healthy habitats and protect biodiversity. Moreover, these technologies offer the potential for rapid alert systems to detect failing food webs or trophic systems and excessive human interference. Satellite tracking technology serves as an effective tool for analyzing and visualizing data on species inhabiting inaccessible environments, thereby identifying areas requiring conservation practices.
Advancements in multi- and hyperspectral remote sensing have facilitated the mapping and monitoring of critical habitats, such as mangroves, to support urgent conservation efforts. These systems offer comprehensive insights into the composition and health of ecosystems. For example, recent research has compiled the progress made in mangrove species mapping using multispectral and hyperspectral imagery over the past decade. Hyperspectral data introduces innovative approaches for data analysis and can be applied to biodiversity mapping, with a focus on employing scientifically robust data collection techniques.
High-tech mapping
High-tech maps are playing a crucial role in protecting biodiversity by providing valuable insights into species movements, threats, and habitat preservation. For instance, some mapping tools use supercomputers and GIS-based technologies to predict the movement of plants, birds, and mammals as they adapt to climate change. This information allows governments to make informed decisions about conservation planning across borders.
Moreover, certain metrics use satellite data and wildlife surveys to assign a risk score to each species, indicating their risk of extinction and the human activities causing it. This helps identify the actions needed to protect these species. Mapping ecosystems rich in carbon and biodiversity, such as mangroves, wetlands, and old-growth forests, helps prioritize areas for conservation to combat climate change and preserve biodiversity.
Motion-capture camera systems provide real-world insights into the lives of elusive and secretive animals, which can be used to guide conservation policies. Some technologies use machine learning to process and analyze images from motion-detector cameras, providing near-real-time information about species’ conditions. Lastly, monitoring tools can track legal changes to protected lands and waters, highlighting the impacts of these decisions on biodiversity and people. By leveraging these advanced tools and high-tech maps, we can better understand and protect our planet’s biodiversity.
Drones, Sensors, Cameras, and Satellite Technology
Drones, sensors, cameras, low-power radio networks, and satellite technology can remotely monitor wildlife behavior and habitat changes in real-time, providing valuable information that can be used to stop illegal poaching and habitat destruction. By tracking and monitoring the environment down to the level of individual animals, conservationists can detect threats to biodiversity and respond quickly to protect endangered species and their habitats. These technologies also offer a non-invasive way to study wildlife, reducing the stress on animals and minimizing the impact of human presence in their ecosystems.
Ensuring Accessibility and Affordability of Conservation Technology
Most technology for conservation is developed in rich countries, while most biodiversity is concentrated far away in poorer countries. This discrepancy highlights the need to ensure that technology for conservation is accessible and affordable to all countries to help conserve biodiversity.
Ensuring accessibility and affordability of conservation technology in developing countries can be achieved through several measures. One approach is to make technology openly accessible and more affordable. This can be done by providing funding for research and development of conservation technology in developing countries. Another approach is to provide training and technical support to people on the ground, such as park rangers or land managers, to ensure that they can use and maintain the technology effectively. The use of open-source platforms can also help put knowledge in the hands of people on the ground. Additionally, it is important to understand the needs and constraints of users in developing countries to ensure that conservation technology is designed to meet their needs. This can be achieved through community-sourced assessments of the state of conservation technology. Finally, richer countries can assist poorer ones by providing broader mechanisms for funding and support.
By fostering international collaboration, sharing knowledge and resources, and investing in capacity-building initiatives, the global community can work together to leverage technology for the benefit of biodiversity conservation worldwide.
Conclusion:
Technology offers a wide array of tools and methods that can significantly contribute to the conservation of biodiversity. From satellite imagery and remote sensing to drones and advanced mapping techniques, these technologies can provide valuable information and insights to guide conservation efforts. However, it is crucial to ensure that these technologies are accessible and affordable to all countries, so that the benefits of technology can be realized across the globe in the quest to protect our planet’s precious biodiversity.
Next Steps
Round Table Environmental Informatics (RTEI) is a consulting firm that helps our clients to leverage digital technologies for environmental analytics. We offer free consultations to discuss how we at RTEI can help you.